Master AACN CCRN-Adult Exam with Reliable Practice Questions
A patient who survives near-drowning develops hypoxia-induced cerebral edem
a. Interventions should include
Correct : A
Hypoxia-induced cerebral edema after a near-drowning incident can be managed by administering osmotic diuretics like mannitol. These medications help reduce intracranial pressure by drawing fluid out of the brain tissue and into the bloodstream, thereby alleviating cerebral edema. Maintaining a MAP of 60-70 mm Hg may not be sufficient to address the elevated intracranial pressure, keeping the patient flat could worsen cerebral edema, and hyperventilation with a PaCO2 of 40-45 mm Hg is not typically recommended for managing increased intracranial pressure as it can lead to vasoconstriction and decreased cerebral perfusion. Reference: = CCRN Exam Handbook, AACN Adult CCRN Certification Review Course
Start a Discussions
A patient is admitted with an acute anterior wall MI. Initial hemodynamic readings are:

The nurse anticipates initiating a plan of care for
Start a Discussions
A patient develops the dysrhythmia shown below:
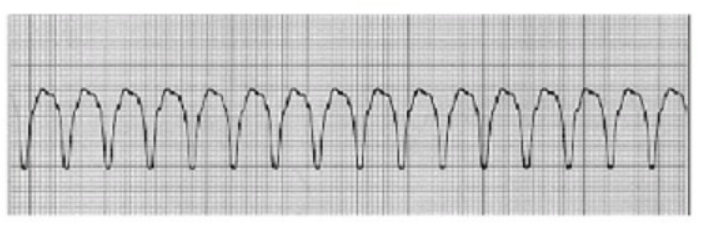
Blood pressure is 83/40. The patient is pale, diaphoretic, lethargic, and disoriented. The most appropriate treatment is
Start a Discussions
Which of the following are physiologic effects of pulmonary contusion?
Start a Discussions
A nurse is caring for a patient who had a gastric bypass procedure 2 days ago. A physician has ordered a gastric tube to be placed due to increased abdominal distention. The nurse realizes that this procedure will most likely need to be done
Start a Discussions