Master NCARB PDD Exam with Reliable Practice Questions
The walls of typical light wood-frame buildings can most economically be made resistive to lateral shear forces, without major alteration to the existing structure, through the use of which one of the following?
Correct : B
For light wood-frame buildings, the most economical way to develop lateral shear capacity---often without major structural alteration---is to add/upgrade wood structural panel (plywood/OSB) shear walls fastened to studs and plates per nailing schedules. This provides diaphragm and wallshear resistance with minimal added framing.
A . Moment connections in wood are labor-intensive and uncommon in light framing.
C . Horizontal board sheathing provides limited shear compared to plywood.
D . Gusset plates do not create a continuous shear diaphragm/wall.
PDD refs: AWC SDPWS (wood shear walls & diaphragms); ARE 5.0 PDD---Structural systems for lateral loads in light-frame construction; IBC Ch. 23.
Start a Discussions
Refer to the exhibit.
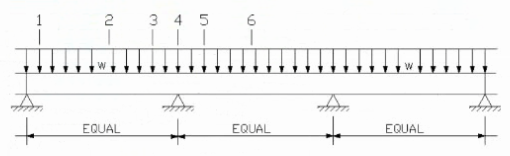
Refer to the exhibit.
It is required to cut a hole in the web of the beam shown.
Which of the locations would be best? Check the two that apply.
Correct : B, D
Cutting holes in beam webs is common for running mechanical, electrical, or plumbing services but must be done carefully to avoid weakening structural integrity.
Holes should be located near mid-span supports (points of low bending moment and high shear) to reduce impact on beam bending strength.
Holes should not be located near areas of maximum bending moment (typically mid-span between supports), because this is where the beam experiences maximum tension or compression.
Locations 2 and 4 are at or near the beam supports (shear zones), and generally small holes can be cut there, following size limits and reinforcement guidelines.
Locations 1, 3, and 5 are closer to mid-span or areas of high bending stress, so holes here risk compromising the beam's moment capacity.
NCARB ARE 5.0 Review Manual, Structural Systems chapter
Steel construction and beam design guidelines (AISC)
Building codes and structural engineering best practices for web penetrations
Start a Discussions
Proposed trees along a residential street next to a new development site should first be selected based on which of the following?
Correct : B
Selecting trees for residential streets near a new development should prioritize:
Adaptability to local climate and soil conditions to ensure healthy growth and longevity.
While seasonal foliage, color, scale, and wildlife habitat are important, they are secondary to ensuring the tree can survive and thrive in the environment.
Dense root systems and wind resistance are considerations but often come after adaptability is confirmed.
NCARB ARE 5.0 Review Manual, Site Design and Environmental Systems chapter
Landscape architecture best practices and local planting guides
Start a Discussions
Refer to the exhibit.
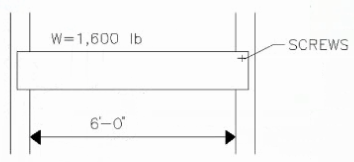
Refer to the exhibit.
Using metal stud framing, how many screws per stud are needed to connect the header if each screw is rated at 440 pounds for shear and 215 pounds for tension?
Correct : B
Given:
Load (W) = 1,600 lb
Screw shear capacity = 440 lb per screw
Screw tension capacity = 215 lb per screw
Assuming worst case is shear capacity (usually governs):

If tension applies, 8 screws needed.
But typically, shear governs for header connection; since question likely focuses on shear, 4 screws would be safest.
If question expects minimal number to resist both, 8 screws would be correct.
Final answer: 4 screws (Option C) if shear governs; if considering tension also, 8 screws (Option D).
Since the question is ambiguous, and shear usually controls, C. 4 screws is appropriate.
NCARB ARE 5.0 Review Manual, Structural Systems chapter
Metal stud framing connection design standards
Start a Discussions
Refer to the exhibit.
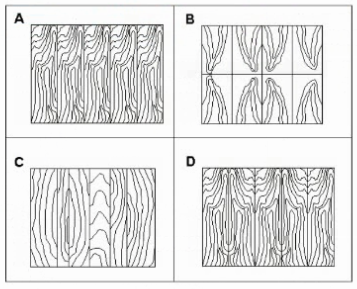
Refer to the exhibit.
Which of the following examples of wood paneling depicts the method of "slip matching" between adjacent wood veneers?
Correct : A
Understanding Slip Matching in Wood Veneer
When wood veneer is sliced from a log, each sheet (or 'leaf') has a repeating grain pattern. How those sheets are arranged side-by-side on a panel is called the matching method.
Slip Matching:
Consecutive leaves are laid side-by-side without flipping or reversing them.
This creates a repeating grain pattern that flows consistently across the panel.
The result is a uniform, continuous grain with no 'mirror image' effect --- the cathedrals and figure in the grain run in the same direction from sheet to sheet.
Slip matching often produces a striped effect if the grain is straight, or a flowing, consistent repeat if the grain is more figured.
Identifying Slip Matching in the Exhibit:
Option A shows consecutive veneer leaves with the grain pattern running in the same orientation across the panel --- no mirroring, only repetition. This is classic slip match.
Option B shows book matching --- where every other leaf is flipped horizontally to create a mirrored grain pattern.
Option C appears to be random matching --- leaves are placed without grain sequence alignment.
Option D shows reverse slip matching --- similar to slip match but alternating leaves are reversed end-to-end.
NCARB ARE 5.0 PDD Study Guide Reference:
Content Area: Integration of Materials & Finishes --- Millwork and Casework Veneer Matching Methods
Sources:
Architectural Woodwork Standards (AWS) --- Section on Veneer Matching
Architectural Graphic Standards --- Finish Carpentry and Veneer Matching
Building Construction Illustrated (Ching) --- Interior Finish Carpentry
Key Point: Slip matching keeps all veneer leaves in the same orientation, producing a consistent flow of the grain without the mirrored effect seen in book matching.
Start a Discussions